To copy data from one field (column) to another field within the same table in MySQL, you use the UPDATE statement.
Syntax Code:
UPDATE SET = WHERE Condition;
Explanation of the above syntax:
Table_Name: Replace this with the actual name of your table.
Target_Column: Replace this with the name of the column where you want to copy the data to.
Source_Column: Replace this with the name of the column from which you want to copy the data from.
WHERE Condition (Optional): This clause specifies which rows should be updated. If you omit the WHERE clause, the data from Source_Column will be copied to Target_Column for all rows in the table. Use a WHERE clause to target specific rows based on a condition.
Example:
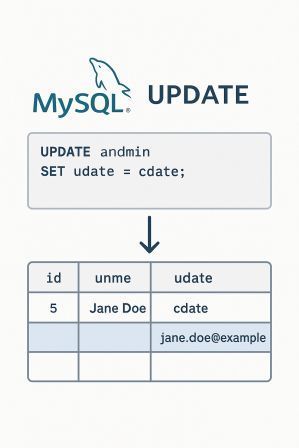
Suppose you have a table named admin with columns cdate and udate. You want to copy the values from cdate into udate for all admin rows.
The code is below.
UPDATE admin SET udate = cdate;
with where clause
UPDATE admin SET udate = cdate WHERE cdate !=”;
Important Considerations:
Data Types: Ensure that the data types of the Source_Column and Target_Column are compatible. MySQL will attempt to convert data types if they are different, but this can lead to errors or data loss if the conversion is not possible or results in truncation.
Backup: Before performing any UPDATE operation on a live database, it is highly recommended to create a backup of your data.
WHERE Clause: Be very careful with your WHERE clause. A mistake here can lead to unintended data changes across your entire table.
Leave a Reply